Deployment and Release
Environments
The process of releasing vlayer spans across four environments:
- User Environment - web browsers
- Developer Environment - Tools and libraries on the developer's local machine
- vlayer Node Infrastructure - Consists of various server types
- Blockchain Networks - Smart contracts deployed across multiple chains
The diagram below illustrates these environments, along with associated artifacts and key interdependencies:
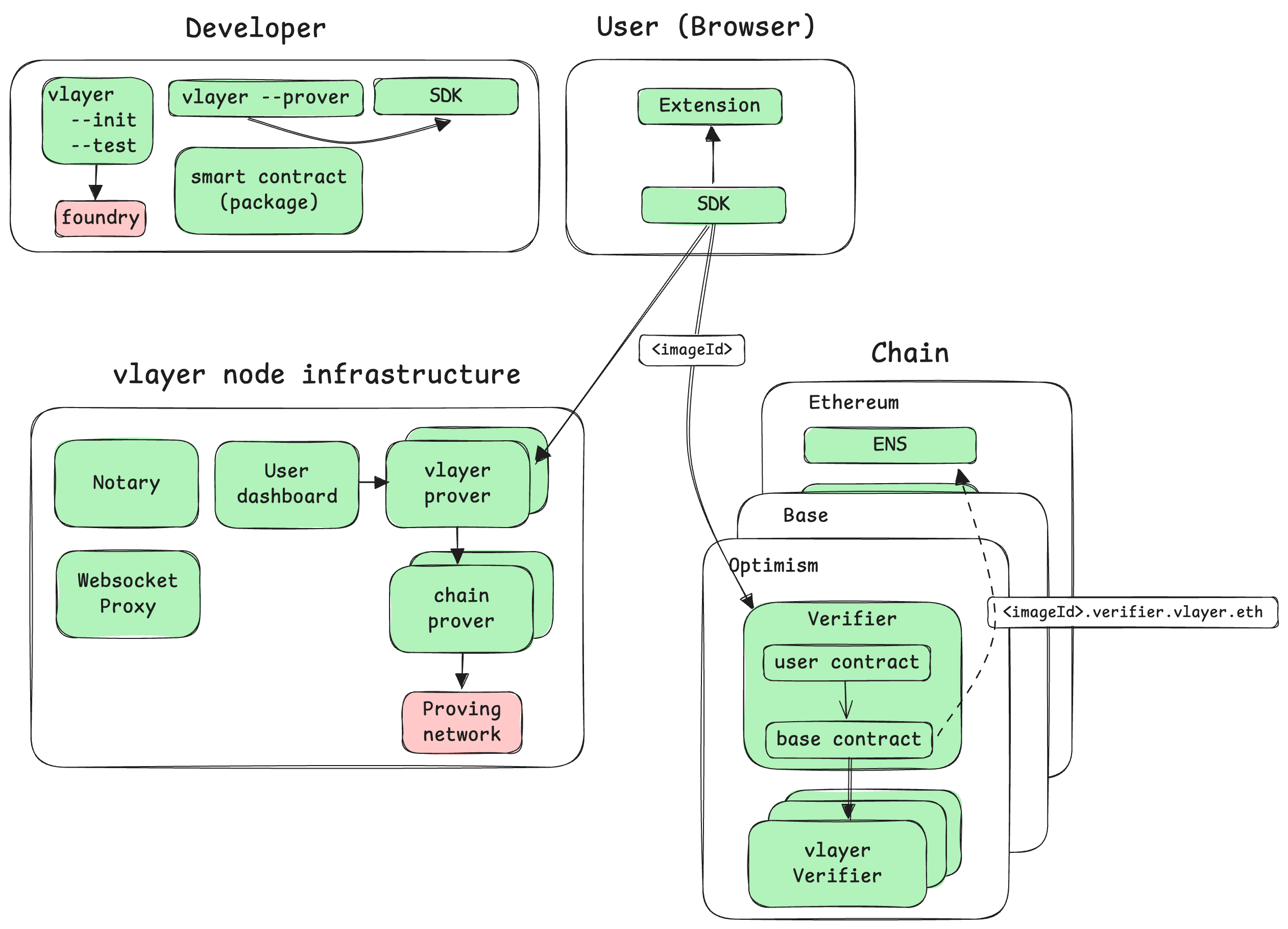
User Experience
From a delivery perspective, the key aspects of user experience are:
- Reliable, functioning software
- Clear error messages when issues arise
- An easy update process for deprecated software
Users primarily interact with two main artifacts:
- The SDK, embedded within the developer's web application
- The developer's smart contracts, which interface with vlayer smart contracts
- Optionally, a browser extension if the user is engaging with Web Proofs
Unfortunately, both the user and vlayer have limited control over the SDK version in use. The SDK is implemented by the developer and updated only at the developer’s discretion.
Developer Experience
Nightly and Stable Versions
To ensure developers have the best possible experience, we recommend always using the most recent version of vlayer.
A nightly version is published daily and stable version is released regularly and includes tested features and fixes.
- Developers have access to the latest features and bug fixes.
- We can guarantee compatibility among various artifacts.
A potential downside of this approach is that it may require developers to address bugs in their code caused by breaking changes in vlayer.
We recommend using stable version for production. Use nightly versions if you're developing integrations or need early access to new features.
Artifacts and Deployment Cycles
Each environment includes multiple artifacts, each with distinct deployment cycle limitations, as detailed below.
User Environment
- SDK
- Release: vlayer releases new SDK versions in nightly and stable channels.
- Installation: Developers add the SDK to their project dependencies.
- Updates: Neither vlayer nor the user can enforce SDK version updates, making SDK updates the least controllable in terms of version management on the user's end.
Developer Environment (Command Line Tools)
- vlayer Command Line Tools - Used in different contexts:
vlayerwithinitandtestflags, tightly integrated with Foundrycall_server, an optional dependency for local development without relying on the vlayer node infrastructure for proving
- Local Development SDK
- vlayer Smart Contracts - Managed via Soldeer
- Foundry - An external dependency requiring updates synchronized with vlayer to:
- Ensure
testandinitcommands operate in the same directory asforgeand other tools - Support the latest REVM (Rust Ethereum Virtual Machine) changes, including hard-fork and network compatibility
- Ensure
Updating these artifacts is encouraged and is executable via vlayer update.
Blockchain Networks (Smart Contracts)
- User’s Smart Contract - Derived from the
Verifierbase class, with deployment managed externally - Verifier Helper Smart Contract - Soldeer package released in Nightly/Stable cycle. Most important contracts are deployed at stable addresses.
vlayer Node Infrastructure (Servers)
- User Dashboard - A user interface for managing proof history and purchasing
- vlayer Prover - A server for executing
Proveroperations - Chain Indexers - A server for maintaining a Chain Proof Cache, including a JSON RPC server and worker components
- TLS Notary Server - Manages notarization in the Web Proofs context, deployed as needed
- DNS Notary Server - Manages notarization in the Email Proofs context, deployed as needed
- WebSocket Proxy - Handles TCP/IP connection proxying for Web Proofs, deployed as required
- Additional Components - Includes monitoring infrastructure and networked proving systems
All server infrastructure may undergo daily deployments to accommodate updates.
| Artifact | Destination | Release Frequency | Installation/Update Method | Update Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Environment | ||||
| SDK | Developer's app | Uncontrollable | npm install | Uncontrollable |
| Developer Environment | ||||
| Smart Contracts package | Soldeer | Nightly/Stable | soldeer / vlayer update | Developer |
| vlayer CLI + prover | GitHub | Nightly/Stable | vlayerup / vlayer update | Developer |
| SDK (local) | npm | Nightly/Stable | npm install / vlayer update | Developer |
| Foundry | As needed | foundryup | Developer | |
| Blockchain Networks | ||||
| User's contracts | Blockchain | Uncontrollable | soldeer install | Uncontrollable |
| vlayer contracts | Blockchain | Nightly/Stable | - | vlayer |
| vlayer Node Infrastructure | ||||
| User dashboard | Server | Daily | - | vlayer |
| vlayer prover | Server | Nightly/Stable | - | vlayer |
| Chain Indexers | Server | Stable | - | vlayer |
| Notary Servers (TLS/DNS) | Server | As needed | - | vlayer |
| WebSocket proxy | Server | As needed | - | vlayer |
| Proving network (Bonsai) | Server | Uncontrollable | - | Uncontrollable |